Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. This can cause pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers. If these symptoms are severe and do not respond to other treatments, such as splinting or physical therapy, surgery may be recommended. Dr. Leena Jain, one of the best plastic surgeon in Mumbai has shared the symptoms, causes and treatment of the carpal tunnel syndrome in this article.
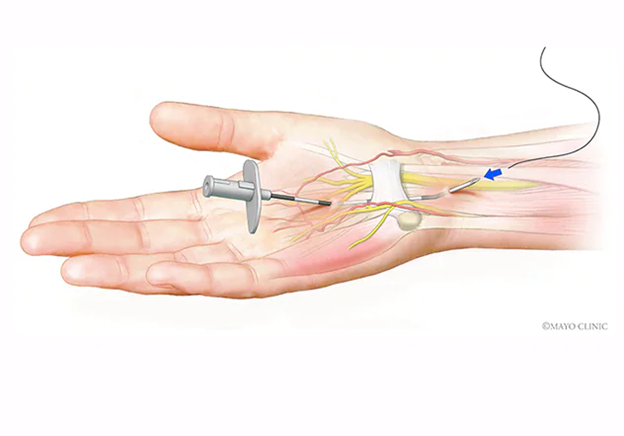
Carpal tunnel surgery, also known as carpal tunnel release surgery, is a procedure that is done to relieve pressure on the median nerve and alleviate the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. The surgery is typically performed by an orthopedic surgeon or a hand surgeon.
Let’s discuss the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome below,
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. This can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers, particularly the thumb, index, middle, and half of the ring finger
- Difficulty gripping objects or making a fist
- A feeling of “pins and needles” in the hand
- A loss of strength in the hand and fingers
- Difficulty performing fine motor tasks, such as buttoning a shirt or tying shoelaces
- Pain or discomfort that radiates up the arm
These symptoms often occur at night or when the wrist is bent, and they may get worse over time. In severe cases, carpal tunnel syndrome can cause muscle wasting in the hand and fingers.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor or a hand specialist. They can diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome and recommend treatment options, such as splinting, physical therapy, or surgery. Early treatment can help to alleviate your symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
Causes of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. The median nerve is responsible for providing sensation to the palm side of the thumb, index, middle, and half of the ring finger, and for controlling some of the muscles in the hand.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome, including:
- Anatomical abnormalities: People with smaller carpal tunnels or those who have a wrist joint that is slightly out of alignment may be more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Repetitive hand and wrist movements: Jobs or activities that involve repeated hand and wrist movements, such as typing, using a mouse, or assembly line work, can put stress on the median nerve and increase the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy can cause fluid retention, which can increase pressure on the median nerve and lead to carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid disorders, can increase the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Injuries: Wrist fractures or sprains can damage the median nerve and cause carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Age: The risk of carpal tunnel syndrome increases with age.
If you are experiencing symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome and are concerned about the potential causes, it is important to see a doctor or a hand specialist. They can assess your individual situation and help determine the cause of your symptoms.
Diagnosis
Carpal tunnel syndrome is usually diagnosed based on a combination of factors, including a physical examination, a review of your medical history, and certain diagnostic tests.
During a physical examination, your doctor will ask about your symptoms and how they are affecting your daily activities. They will also examine your hands, wrists, and arms, looking for any signs of swelling, tenderness, or weakness. They may also ask you to perform certain hand and finger movements to assess your range of motion and strength.
Your doctor may also ask about your work or recreational activities, as certain activities that involve repetitive hand and wrist movements, such as typing or using a mouse, can increase the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor may also order certain diagnostic tests, such as:
- Nerve conduction studies: This test measures how well and how quickly electrical signals pass through the median nerve.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test measures the electrical activity of the muscles in the hand and forearm.
- X-rays: X-rays can help to rule out other conditions, such as arthritis or a wrist fracture, that may be causing your symptoms.
Based on the results of these tests and the overall evaluation, your doctor can diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome and recommend treatment options. It is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to help alleviate your symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
Treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome
There are several treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome, and the best option will depend on the severity of your symptoms and the underlying cause of your condition. Treatment options may include:
- Non-surgical treatments: These treatments may include splinting the wrist to keep it in a neutral position, taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation, and avoiding activities that may worsen your symptoms. Physical therapy or occupational therapy may also be recommended to help improve strength and flexibility in the wrist and hand.
- Corticosteroid injections: These injections can help to reduce inflammation and swelling around the median nerve, relieving pressure on the nerve.
- Surgery: If non-surgical treatments do not provide adequate relief, surgery may be recommended. During the procedure, called carpal tunnel release surgery, the surgeon will make a small incision in the wrist and divide the transverse carpal ligament, which is a band of tissue that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel. This will create more space for the median nerve and the tendons that run through the carpal tunnel, relieving the compression on the nerve.
Your doctor will work with you to determine the best treatment option based on the severity of your symptoms, your overall health, and your lifestyle. It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations and to seek treatment as soon as possible to help alleviate your symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
Conclusion
Overall, carpal tunnel surgery is generally safe and effective at relieving the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. However, as with any surgery, there are some risks, such as infection, nerve damage, or bleeding. Your surgeon will discuss the potential risks and benefits of the surgery with you before the procedure, and will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
If you are experiencing symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome and are considering surgery, it is important to talk to your doctor about your options. Your doctor will be able to assess your individual situation and determine if surgery is the best course of treatment for you. Together, you can come up with a plan to help alleviate your symptoms and improve your quality of life.