Whether or not to undergo pre-implantation genetic testing (PGT) is a personal decision that should be made by individuals in consultation with their healthcare provider and, if applicable, a genetic counselor. There are many factors to consider when deciding whether to undergo PGT, including an individual’s personal and family medical history, their personal values and beliefs, and the potential risks and benefits of the procedure.
If you are considering PGT, it is important to discuss your options with your healthcare provider and, if applicable, a genetic counselor, says Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, one of the best IVF doctor in Mumbai. They can help you understand the potential risks and benefits of the procedure and assist you in making an informed decision about whether or not to undergo PGT.
Who will benefit from Pre-Implantation Genetic Testing?
Pre-implantation genetic testing (PGT) may be beneficial for individuals who have a family history of genetic disorders or who are at an increased risk of having a child with a genetic disorder due to their personal medical history. It may also be beneficial for individuals who have experienced recurrent pregnancy loss or infertility, as PGT can help identify embryos that are genetically healthy and have a higher chance of resulting in a successful pregnancy.
PGT is typically performed in conjunction with in vitro fertilization (IVF). It can be used to screen embryos for a wide range of genetic disorders, including chromosomal abnormalities (such as Down syndrome) and inherited genetic disorders (such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia). It can also be used to screen for certain types of cancer predisposition genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2. By identifying embryos that do not carry these genes, PGT can help prevent the transmission of cancer predisposition to the next generation.
How Long Does Pre-Implantation Genetic Testing take?
Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, top IVF doctor in Mumbai says, the pre-implantation genetic testing (PGT) process typically takes several weeks to complete.
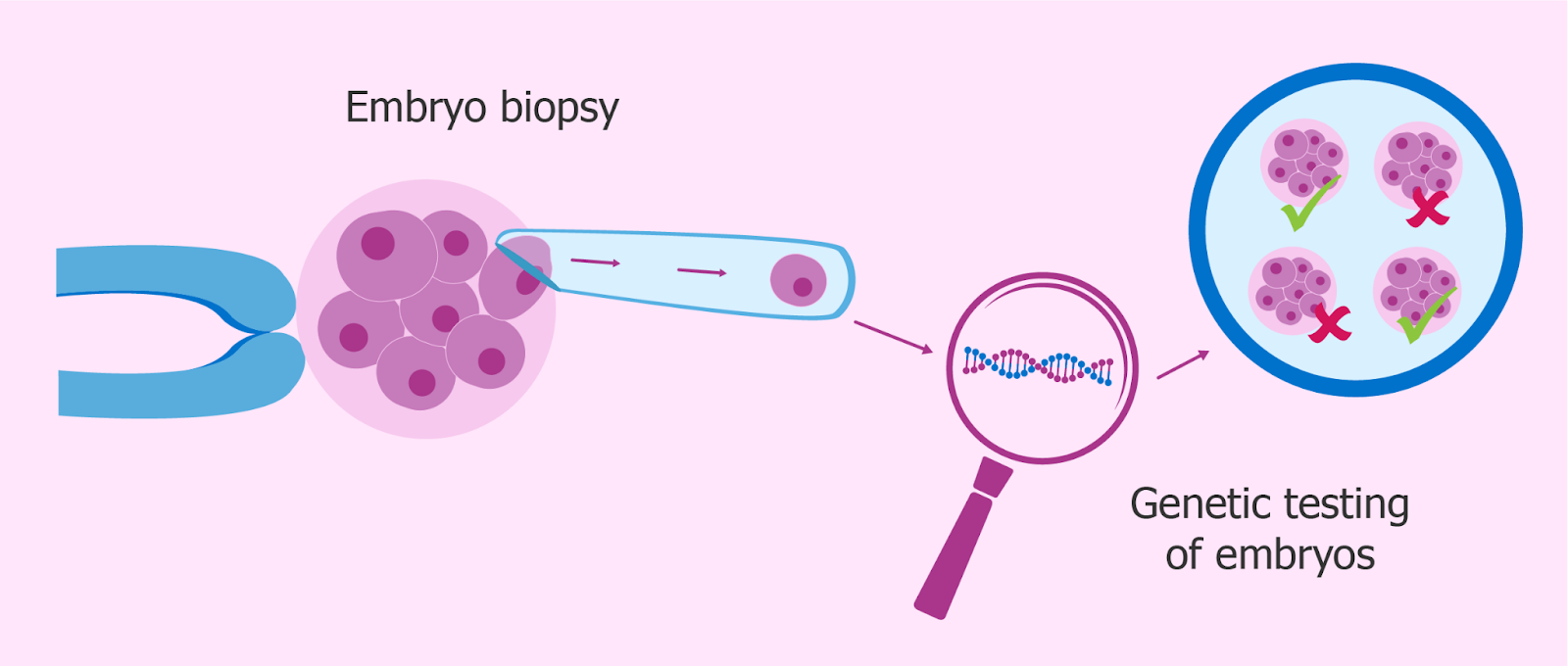
The first step in the PGT process is to undergo in vitro fertilization (IVF), which involves the fertilization of an egg with sperm in a laboratory setting. This typically takes about two weeks, including the time needed for ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval.
Once the embryos have reached the blastomere or blastocyst stage (typically three to five days after fertilization), a small number of cells are removed for testing. This is usually done through a procedure called blastomere or blastocyst biopsy.
The cells are then sent to a laboratory for testing, which can take several days to a week. Once the results of the testing are available, they are shared with the individual or couple and their healthcare provider.
Based on the results of the testing, a decision is made about which embryos to transfer back into the uterus. If an embryo is selected for transfer, it is typically done within a week of the biopsy procedure.
Overall, the entire PGT process can take several weeks to complete, depending on the specific circumstances of the individual or couple. If you have any queries relating to the process of pre-implantation genetic testing ou ask the doctors here.
Complications of Pre-Implantation Genetic Testing
Pre-implantation genetic testing (PGT) is a complex and expensive procedure that carries a small risk of causing harm to the embryo. Some of the potential complications of PGT include:
- Embryo loss: There is a small risk that the procedure will result in the loss of the embryo.
- Inaccurate results: There is a risk that the results of the testing will be inaccurate or inconclusive. This can lead to the transfer of an unhealthy embryo, or the decision to not transfer an embryo that is actually healthy.
- Ethical concerns: There are many ethical concerns surrounding PGT, including issues related to access, cost, and the potential for “designer babies.”
- Emotional stress: The decision to undergo PGT and the process of undergoing the procedure can be emotionally stressful for individuals and couples.
What is the success rate of ivf after pre-implantation genetic testing?
The success rate of in vitro fertilization (IVF) after pre-implantation genetic testing (PGT) can vary depending on a number of factors, including the underlying cause of infertility, the woman’s age, and the specific type of PGT being performed.
PGT can be used to screen for a variety of genetic abnormalities in embryos, including chromosomal abnormalities and inherited genetic disorders. By identifying genetically healthy embryos, PGT can increase the chances of a successful IVF outcome.
According to the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART), the overall live birth rate for IVF with PGT is approximately 50-60% per transfer. This is higher than the live birth rate for IVF without PGT, which is approximately 40% per transfer.
It is important to note that the success rate of IVF with PGT can vary significantly from one individual to another, and it is not always possible to predict the outcome of the procedure. It is important for individuals to discuss the potential risks and benefits of PGT with their healthcare provider and, if applicable, a genetic counselor.