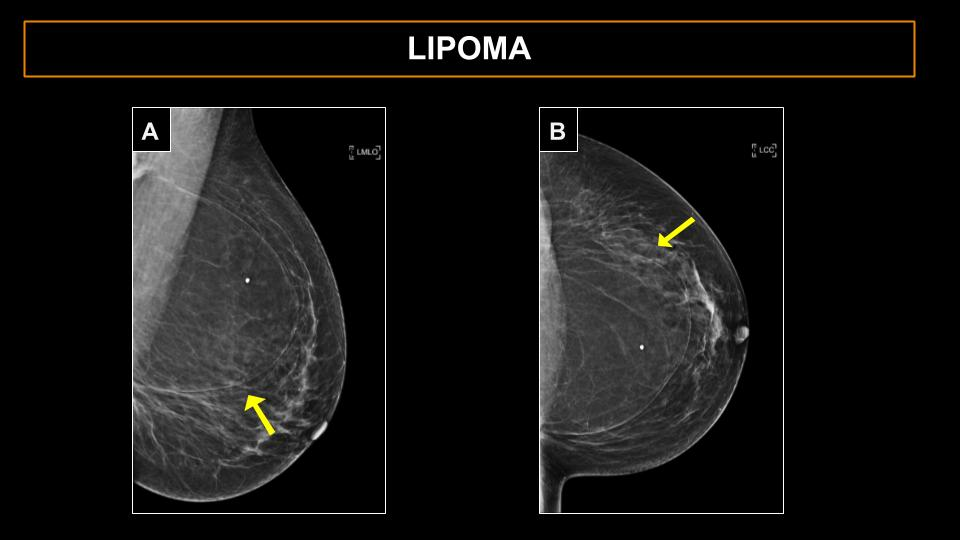
A breast lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor made up of fat cells that occurs in the breast tissue. Lipomas are usually slow-growing and soft to the touch, and they are often movable under the skin. They are usually not painful. Breast lipomas are most common in women over the age of 40.
Breast lipomas can be diagnosed through a physical examination and imaging tests such as mammography or ultrasound. In most cases, no treatment is necessary if the lipoma is small and not causing any symptoms. However, if the lipoma is causing discomfort or is of concern for any other reason, it can be removed surgically. The surgical procedure used to remove a lipoma is called a lipoma excision.
It is important to pay attention to any changes in the breasts or if you see or feel any breast lumps and to seek medical attention if you have any concerns. Early detection of breast abnormalities can help ensure timely treatment and the best possible outcome.
In this article we shall see the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of breast lipoma as explained by Dr. Garvit Chitkara, one of the most prominent breast cancer surgeon in Mumbai.
Lets see the symptoms of breast lipoma below,
Symptoms of Breast Lipoma
The most common symptom of a breast lipoma is a palpable lump in the breast tissue. Lipomas are usually slow-growing and soft to the touch, and they are often movable under the skin. They are usually not painful. Other symptoms of a breast lipoma may include changes in the shape or appearance of the breast, breast pain or tenderness, or discharge from the nipple.
It is important to note that these symptoms do not necessarily mean that a person has a breast lipoma. It is always important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. Early detection of breast abnormalities can help ensure timely treatment and the best possible outcome.
Diagnosis of Breast Lipoma
The diagnosis of a breast lipoma is usually made through a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. During a physical examination, the healthcare provider will feel for any lumps or abnormalities in the breast tissue. They may also recommend imaging tests such as mammography or ultrasound to get a better view of the breast tissue and to confirm the diagnosis. To know more about diagnosis of breast lipoma click here at clinicspots.
In some cases, the healthcare provider may recommend a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. During a biopsy, a small sample of tissue is removed and examined under a microscope to determine if it is cancerous or benign.
It is important to consult a healthcare provider if you notice any changes in your breasts or if you have any concerns. Early detection of breast abnormalities can help ensure timely treatment and the best possible outcome.
Treatment of Breast Lipoma
The treatment of a breast lipoma depends on the size and location of the tumor and the individual’s symptoms and preferences. In many cases, no treatment is necessary if the lipoma is small and not causing any symptoms. The healthcare provider may recommend monitoring the tumor with regular breast exams and imaging tests to ensure that it is not growing.
If the lipoma is causing discomfort or is of concern for any other reason, it can be removed surgically. The surgical procedure used to remove a lipoma is called a lipoma excision. During this procedure, the lipoma and a small margin of surrounding tissue are removed.
It is important to discuss the treatment options with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action. In most cases, breast lipomas do not recur after they are removed.
Facts about Breast Lipoma
- A breast lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor made up of fat cells that occurs in the breast tissue.
- Lipomas are usually slow-growing and soft to the touch, and they are often movable under the skin.
- Breast lipomas are most common in women over the age of 40.
- Lipomas are usually not painful.
- Breast lipomas can be diagnosed through a physical examination and imaging tests such as mammography or ultrasound.
- In most cases, no treatment is necessary if the lipoma is small and not causing any symptoms.
- If the lipoma is causing discomfort or is of concern for any other reason, it can be removed surgically.
- It is important to pay attention to any changes in the breasts and to seek medical attention if you have any concerns. Early detection of breast abnormalities can help ensure timely treatment and the best possible outcome.